25-Nov-2023 , Updated on 11/25/2023 6:33:51 AM
The History and the Future of Architecture in the World
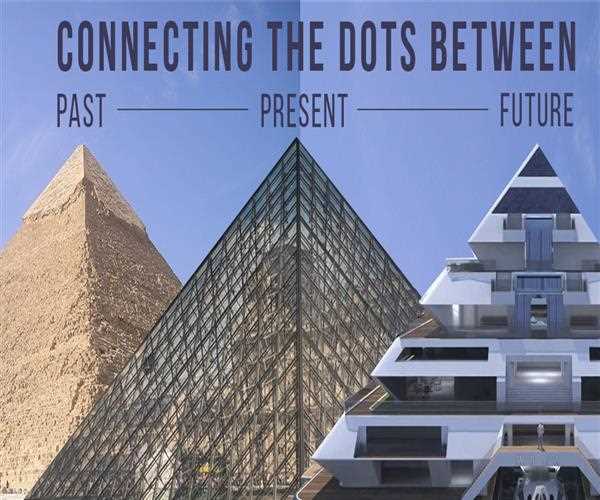
Architecture , as an art form and a practical discipline, has played a pivotal role in shaping the world we inhabit. From ancient civilizations to modern metropolises, architecture reflects the cultural, social, and technological evolution of humanity. This view will delve into the rich history of architecture, exploring its various phases and movements, while also speculating on the future trends that may redefine the built environment.
Historical Evolution of Architecture:
Ancient Civilizations:
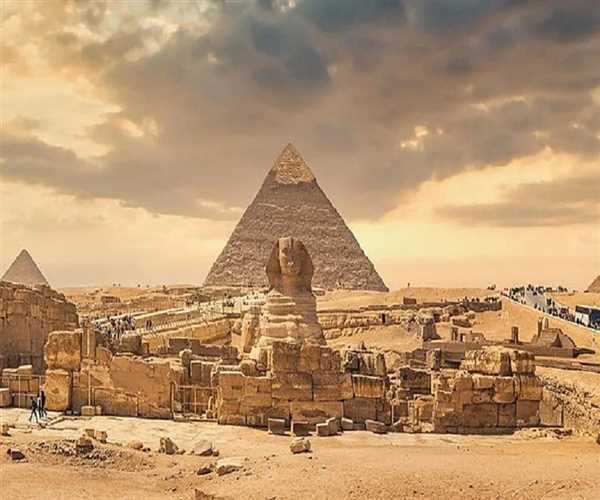
The roots of architecture trace back to the dawn of human civilization . Ancient cultures such as the Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, and Mesopotamians made significant contributions to architectural innovation. The pyramids of Egypt stand as enduring symbols of ancient architectural prowess, showcasing meticulous planning and engineering marvels.

In ancient Greece, the classical orders—Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—emerged, influencing architectural styles for centuries. The Romans, known for their mastery of arches, vaults, and domes, expanded upon Greek principles, creating colossal structures like the Colosseum and the Pantheon.
Medieval Architecture:
The medieval period brought about a shift in architectural styles with the rise of Gothic architecture. Cathedrals like Notre-Dame in Paris and the Canterbury Cathedral in England exemplify the soaring heights and intricate detailing characteristic of this era. The pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses became defining features of Gothic architecture.
Renaissance and Baroque:
The Renaissance witnessed a revival of classical influences, with architects looking to ancient Greece and Rome for inspiration. Filippo Brunelleschi's dome in Florence and Andrea Palladio's villas are quintessential examples of Renaissance architecture, characterized by harmony, proportion, and a focus on symmetry.
The Baroque period that followed embraced dramatic elements, ornate detailing, and a sense of grandeur. Buildings like the Palace of Versailles in France and St. Peter's Basilica in Rome epitomize the opulence and theatricality of Baroque architecture.
19th and 20th Century:
The 19th century witnessed diverse architectural movements, from the neoclassical designs of the early century to the emergence of the industrial-inspired Gothic Revival. The advent of the Industrial Revolution led to new materials and construction techniques, allowing for the creation of iron and glass structures like the Crystal Palace in London.
The 20th century marked a radical departure from traditional styles with the advent of modernism. Architects like Le Corbusier and Frank Lloyd Wright championed functionalism, simplicity, and a break from historical ornamentation. The Bauhaus movement, founded by Walter Gropius, emphasized the fusion of art and industry, giving birth to a new aesthetic that prioritized form following function.
Contemporary Architecture:
Postmodernism and Deconstructivism:
In the latter half of the 20th century, postmodernism emerged as a reaction against the perceived rigidities of modernism. Architects like Robert Venturi and Frank Gehry explored playful forms, historical references, and a departure from strict functionalism. Deconstructivism, championed by architects like Zaha Hadid, introduced fragmented forms and dynamic compositions that challenged conventional notions of structure.
Sustainability and Green Architecture:
As the world grapples with environmental concerns, architecture has embraced sustainability. Green architecture prioritizes eco-friendly design , energy efficiency, and the use of renewable materials. Concepts like passive design, green roofs, and solar panels have become integral to contemporary architectural practices.
Digital and Parametric Architecture:
The 21st century has witnessed the integration of digital technologies into architecture. Computer-aided design (CAD) and parametric modeling allow architects to explore complex geometries and create structures with unprecedented precision. Innovations like 3D printing have the potential to revolutionize construction methods, offering efficient and sustainable alternatives.
The Future of Architecture:
Smart Cities and Responsive Architecture:
As urbanization accelerates, architects are tasked with creating smarter and more responsive cities. The integration of technology, data analytics , and artificial intelligence has the potential to transform urban spaces. Responsive architecture adapts to changing environmental conditions, optimizing energy usage and enhancing the overall quality of urban life.
Adaptive Reuse and Circular Economy:
In the face of environmental challenges, architects are increasingly turning to adaptive reuse as a sustainable practice. Converting existing structures for new purposes reduces the demand for new construction and minimizes waste. The circular economy concept, which promotes the reuse and recycling of materials, is gaining traction, reshaping the way architects approach design and construction.
Biophilic Design and Well-being:
Biophilic design, incorporating natural elements into the built environment, is gaining prominence. The recognition of the impact of the built environment on mental health and well-being has led architects to prioritize designs that foster a connection with nature. Green spaces, natural light, and ventilation are integral components of this approach, aiming to create healthier and more nurturing spaces for occupants.
Innovative Materials and Construction Techniques:
The future of architecture is intertwined with advancements in materials and construction techniques. From self-healing concrete to biofabricated materials, architects are exploring innovative solutions that enhance durability, reduce environmental impact, and open up new possibilities in design. Prefabrication and modular construction are becoming increasingly popular, offering efficiency and flexibility in the building process.
Space Architecture:
As humanity looks beyond Earth, architects are pondering the design challenges of extraterrestrial habitats. Space architecture involves conceptualizing structures suitable for the Moon, Mars, or even space stations. This futuristic branch of architecture explores the intersection of technology, sustainability, and human adaptability in the harsh environments of outer space.
Conclusion:
Architecture, throughout history, has been a mirror reflecting the aspirations, values, and technological capabilities of societies. From the grandeur of ancient civilizations to the innovative spirit of the present, architects have shaped the world we inhabit. As we stand at the threshold of the future, the challenges of sustainability, technological integration, and the quest for well-being will undoubtedly influence the trajectory of architectural evolution.

SEO and Content Writer
I am Drishan vig. I used to write blogs, articles, and stories in a way that entices the audience. I assure you that consistency, style, and tone must be met while writing the content. Working with the clients like bfc, varthana, ITC hotels, indusind, mumpa, mollydolly etc. has made me realized that writing content is not enough but doing seo is the first thing for it.
Join Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive emails about new views posts, releases and updates.
Copyright 2010 - 2026 MindStick Software Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Cookie Policy