10-Aug-2023 , Updated on 8/10/2023 6:02:09 AM
Birth and death of the stars
Highlights
The formation of a star-
- Stars are born from regions, in space called clouds, where gas and dust come together.
- The force of gravity causes this gas and dust to collapse leading to the birth of a protostar.
- As the contracts it heats up triggering nuclear fusion reactions in its core.
- Once the nuclear reactions stabilize and the star achieves equilibrium it enters its main sequence phase.
Life on the sequence
- The main sequence phase is the period in a stars life. During this phase hydrogen fuses into helium at its core.
- A delicate balance between collapse and energy release from fusion ensures that the star remains stable.
Evolution of stars
- Smaller stars like dwarfs burn their hydrogen fuel slowly. Can survive for trillions of years.
- Medium sized stars like our Sun have a lifespan of billions of years before they deplete their hydrogen fuel.
The demise of a star-
- During the phase medium sized stars expand as they exhaust their cores hydrogen supply.
- Within the core of a giant helium undergoes fusion to form elements such, as carbon and oxygen.
- When a red giant star reaches the end of its life it expels its layers creating a shell made of gas and dust called a planetary nebula.
- After this process what remains of the stars core will. Transform into a white dwarf that is roughly the size of Earth.
- The night sky has forever fascinated beings, with its shimmering stars, formations of constellations and celestial marvels.
Among these entities stars hold a significance as they provide illumination in the vastness of space and play a crucial role in the magnificent cosmic theater. The creation and eventual demise of stars are some of the fundamental processes in the universe.
Let's explores the captivating journey of stars delving into their formation from clouds of gas and dust their evolution through stages and their ultimate passing that leaves behind awe-inspiring remnants and cosmic legacies.
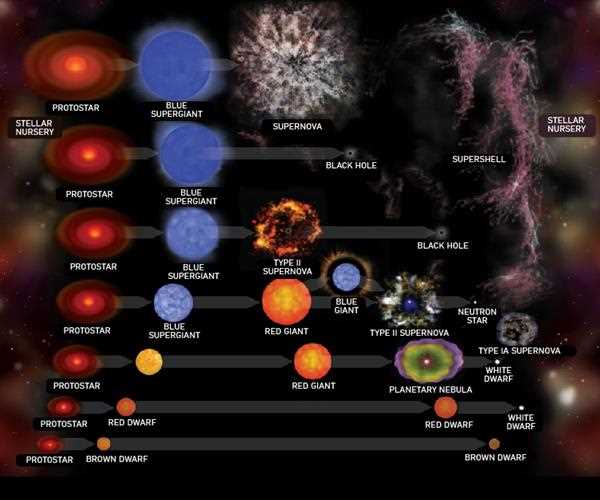
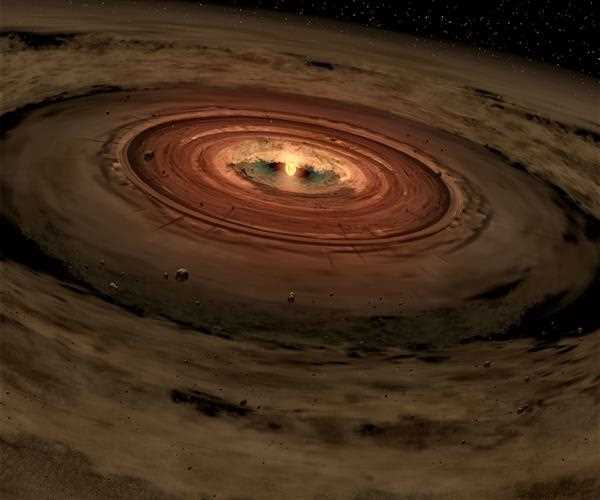
I. The Birthplace of Stars- Stellar Nurseries
At the core of star formation lies clouds known as nebulae that consist of gas and dust spread across galaxies. These nebulae act as nurturing grounds for stars by harnessing the power of gravity. One famous stellar nursery is found in the Orion constellation. Its called the Orion Nebula. Which can be seen with our naked eyes on a clear night.
Within these clouds certain regions known as " cores" begin to take shape with higher densities by gradually accumulating particles of gas and dust . The force exerted by gravity pulls these particles inward causing an increase in density and temperature, within the core until it reaches a point where nuclear fusion ignites. This pivotal moment signifies the birth of a star.

II. Main Sequence Stars- The Adolescence of Stars
Once nuclear fusion initiates, within a stars core it enters a phase known as the sequence. This is considered the most stable period in a stars life cycle. During this stage stars primarily convert hydrogen into helium through fusion releasing an amount of energy in the form of light and heat.
The mass of a star significantly impacts its progression through this phase. Stars with masses than eight times that of our Sun burn their fuel at a faster rate shining brightly but having shorter lifespans. On the hand low mass stars like our Sun lead a relaxed existence steadily burning their fuel for billions of years.
III. Stellar Evolution- Red Giants and Beyond
As a star depletes its hydrogen fuel supply it undergoes a phase of evolution. In the case of to mass stars like our Sun, the core contracts while the outer layers expand resulting in its transformation into a red giant. The outer layers expand to sizes. May even engulf neighboring planets and celestial bodies. The red giant phase is transient, before reaching the stage of evolution.

For high mass stars this particular phase is strikingly dramatic.
As the temperature and pressure increase, the core of a star contracts. This causes elements, like helium, carbon and oxygen to fuse together forming elements such as neon, magnesium and silicon. The fusion process continues as each successive layer combines elements until it reaches iron at the core.
IV. Grand Finale of Stars- Supernovae and What Remains
Once a high mass star forms an iron core fusion reactions cease since iron cannot release energy through fusion. The core collapses due to gravitys pull resulting in a release of energy known as a supernova. A supernovas brightness can surpass that of a galaxy for a period and expels vast amounts of heavy elements into space.
During a supernova event enormous quantities of energy, neutrinos and cosmic rays are generated. This event leaves behind remnants in the form of neutron stars or black holes. Neutron stars are objects that squeeze the mass equivalent to several Suns into a sphere no larger than a city. On the hand
black holes represent regions, in spacetime with forces so intense that nothing can escape their grasp – not even light.
When it comes to stars that have a to medium mass they don't explode like supernovae. Instead they shed their layers creating a shell made of gas and dust called a
planetary nebula. The remaining core, known as a dwarf is dense and hot. Gradually cools down over billions of years eventually turning into a dark and cold "dead star."
V. Stellar Recycling- Nurturing New Beginnings
The remnants of stars whether they be dwarfs neutron stars or black holes play a vital role in the recycling process of the cosmos. When massive stars explode as supernovae they release elements that become part of the medium. This enriches the medium with the building blocks, for stars, planets and even life itself. As a result of this process each new generation of stars emerges with an expanded range of elements.
The birth and death of stars are awe inspiring events that shape the evolution of our universe. From the nurseries where new stars are born to the explosive supernovae that give rise to neutron stars and black holes these celestial entities are truly remarkable. The life cycle of stars not provides us with elements for sustaining life but also offers us a humbling perspective on our place, within the vast cosmos.
As humanity delves further into the study and exploration of bodies our comprehension of the blueprint that shapes our universe expands. This enriches our awe and inquisitiveness towards the wonders residing beyond the boundaries of our planet.

SEO and Content Writer
I am Drishan vig. I used to write blogs, articles, and stories in a way that entices the audience. I assure you that consistency, style, and tone must be met while writing the content. Working with the clients like bfc, varthana, ITC hotels, indusind, mumpa, mollydolly etc. has made me realized that writing content is not enough but doing seo is the first thing for it.
Join Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive emails about new views posts, releases and updates.
Copyright 2010 - 2026 MindStick Software Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Cookie Policy