
10-Jul-2023 , Updated on 7/10/2023 10:20:43 AM
Story of the fiction writer "Leo Tolstoy"
Highlights
- Leo Tolstoy was born on September 9, 1828, in Yasnaya Polyana, Russia.
- He belonged to a noble family and grew up surrounded by literature and education.
- Tolstoy's early works include short stories and novels that gained recognition, such as "Childhood" (1852) and "The Cossacks" (1863).
- His most famous novel, "War and Peace," was published between 1865 and 1869. It is a sprawling epic that explores the lives of various characters against the backdrop of the Napoleonic Wars.
- Tolstoy's next major work, "Anna Karenina" (1877), delves into themes of love, marriage, and societal norms. It is regarded as one of the greatest novels ever written.
- Despite his literary success, Tolstoy experienced an existential crisis and became disillusioned with the privileged life he led. He began to question the purpose of life and turned to moral and spiritual matters.
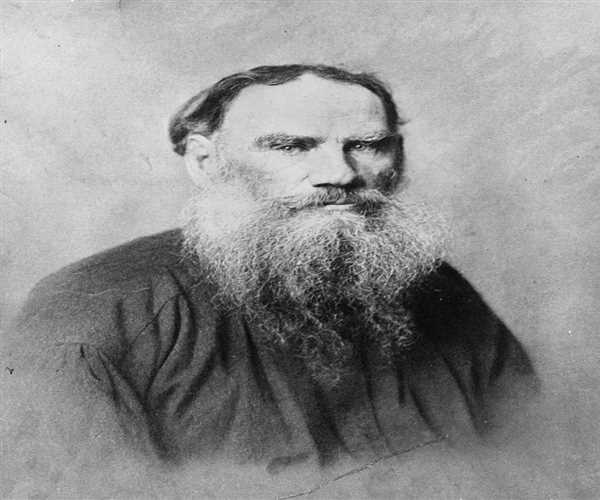
Leo Tolstoy, one of the most renowned and influential authors in literary history, was born on September 9, 1828, in Yasnaya Polyana, Russia. His exceptional storytelling skills and profound understanding of human nature have made him a beloved figure in the world of literature. Tolstoy's works, such as "War and Peace" and "Anna Karenina," have captivated readers for generations, and his ideas on morality, nonviolence, and spirituality continue to resonate with people worldwide.
Early Life and Influences
Tolstoy was born into an aristocratic family and spent his childhood in a rural setting at the family estate. He was raised by his mother after his father's death when he was just nine years old. During his formative years, Tolstoy received education from private tutors and later attended the University of Kazan, where he studied law and oriental languages.
As a young man, Tolstoy was exposed to a wide range of literary works that would shape his writing style and worldview. He avidly read the works of European authors such as Victor Hugo, Charles Dickens, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, whose ideas on social justice and humanism deeply influenced him.
Writing Career
Tolstoy began his writing career in the 1850s, initially producing autobiographical works and short stories. His experiences as a soldier in the Crimean War provided him with material for his first published work, "Sevastopol Sketches" (1855). These vivid and realistic stories portrayed the harsh realities of war and garnered critical acclaim.
In 1862, Tolstoy released "War and Peace," his most celebrated and monumental work. This epic novel, set against the backdrop of the Napoleonic Wars, explores the lives of various Russian aristocratic families and delves into profound themes of love, war, and destiny. With its intricate character development, sweeping narrative, and philosophical musings, "War and Peace" established Tolstoy as a literary genius.
Following the success of "War and Peace," Tolstoy dedicated himself to another masterpiece, "Anna Karenina." Published in 1877, this tragic tale of an unhappily married woman's illicit affair explores the moral and social conventions of 19th-century Russian society. Tolstoy's vivid descriptions, complex characters, and psychological insights into human behavior make "Anna Karenina" a timeless work of literature.
Themes and Philosophy
Tolstoy's writing is not merely a showcase of literary process but also a reflection of his profound philosophical ideas. He delved into themes such as love, death, family, and the search for meaning in life. Tolstoy believed that the purpose of literature was to depict the complexities of human existence and to challenge societal norms and conventions.
Throughout his life, Tolstoy grappled with questions of morality, spirituality, and the pursuit of a meaningful life. His ideas on nonviolence and his advocacy for the rights of the oppressed and the working class influenced later figures such as Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. Tolstoy's philosophy emphasized the importance of simplicity, sincerity, and the rejection of material possessions.
Later Years and Legacy
In the latter part of his life, Tolstoy underwent a spiritual and existential transformation. He renounced his aristocratic lifestyle and embraced a more ascetic existence, adopting principles of Christianity and pacifism. Tolstoy's beliefs often clashed with the Russian Orthodox Church and the autocratic regime, making him a controversial figure.
Tolstoy's later works, such as "The Death of Ivan Ilyich" and "Resurrection," reflect his spiritual journey and explore themes of mortality and redemption. These works showcase Tolstoy's ability to delve into the depths of human emotions and provide profound insights into the human condition.
Leo Tolstoy passed away on November 20, 1910, at the age of 82. His legacy as one of the greatest writers of all time endures to this day. His works continue to inspire countless readers and have been adapted into numerous films and stage productions. Tolstoy's contributions to literature and his profound understanding of the human experience have left an indelible mark on the literary world.
Leo Tolstoy, the Russian author par excellence, revolutionized the literary landscape with his powerful and insightful works. His ability to capture the complexities of human nature and his exploration of timeless themes make him a master of fiction. Tolstoy's writings and philosophy continue to resonate with readers, ensuring that his influence will endure for generations to come.
Beyond his literary achievements, Tolstoy's personal life and convictions also played a significant role in shaping his legacy. His belief in nonviolence and pacifism led him to develop a close bond with Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, who was deeply influenced by Tolstoy's ideas and corresponded with him extensively.
Tolstoy's later years were marked by a deepening sense of social responsibility. He became increasingly concerned with the plight of the poor and the oppressed, and he advocated for social reforms. His essay "What Then Must We Do?" (1886) called for the redistribution of wealth and the establishment of communal societies based on mutual aid and equality. These ideas, along with his commitment to nonviolence, made Tolstoy a source of inspiration for various social and political movements.
Tolstoy's contributions to literature and his impact on society cannot be overstated. His ability to weave intricate narratives while exploring profound philosophical and moral questions made him a literary giant. His works remain relevant and continue to be studied in schools and universities worldwide, offering insights into the human condition and encouraging readers to question societal norms and seek deeper meaning in life.

SEO and Content Writer
I am Drishan vig. I used to write blogs, articles, and stories in a way that entices the audience. I assure you that consistency, style, and tone must be met while writing the content. Working with the clients like bfc, varthana, ITC hotels, indusind, mumpa, mollydolly etc. has made me realized that writing content is not enough but doing seo is the first thing for it.
Join Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive emails about new views posts, releases and updates.
Copyright 2010 - 2026 MindStick Software Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Cookie Policy