
06-Jul-2023 , Updated on 7/6/2023 9:30:16 PM
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and its Impacts on Host Countries
Highlights
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to the investment made by a foreign company or individual in another country with the purpose of establishing a lasting interest and controlling ownership in a business enterprise.
- FDI can have several positive impacts on host countries, including
- Economic growth- FDI can contribute to the host country's economic development by stimulating investment, creating jobs, and enhancing productivity.
- Technology transfer- FDI often brings advanced technologies, managerial expertise, and industry know-how to the host country, helping to upgrade local industries and increase competitiveness.
- Infrastructure development- FDI can lead to the development of infrastructure projects such as roads, ports, and power plants, which can benefit the host country's overall economic development.
- Export promotion- FDI can stimulate exports by improving the host country's production capabilities, access to global markets, and integration into global value chains.
- Tax revenue and government income- FDI can generate tax revenue for the host country, contributing to government finances and public investment in areas such as education, healthcare, and social welfare.
- However, FDI can also have some potential negative impacts on host countries
- Economic dependence- Host countries may become overly reliant on FDI, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in global capital flows and susceptible to the whims of foreign investors.
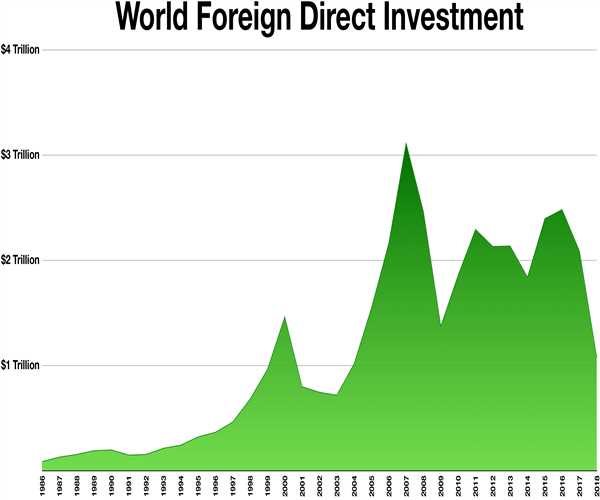
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) refers to the investment made by a company or an individual from one country into business interests located in another country. It is a significant driver of economic growth and development, as it brings in capital, technology, managerial expertise, and access to new markets. Host countries, the recipients of FDI, experience both positive and negative impacts as a result of these investments. This view explores the various effects of FDI on host countries and the factors that influence its impact.
One of the primary benefits of FDI for host countries is the inflow of capital. When foreign investors invest in a host country, they inject funds into the local economy, which can be used for infrastructure development, expansion of businesses, and job creation. This infusion of capital can help stimulate economic growth, enhance productivity, and create employment opportunities for the local population. Additionally, FDI often brings with it technology transfers, as multinational corporations (MNCs) introduce new production techniques, managerial expertise, and advanced technologies to host countries.
Furthermore, FDI can act as a catalyst for industrialization in host countries. MNCs often establish production facilities, which contribute to the growth of local industries. This spillover effect occurs when the presence of MNCs in a particular sector leads to the development of related industries. For example, if a multinational automobile company sets up a manufacturing plant in a host country, it can lead to the growth of ancillary industries such as component suppliers, transportation services, and maintenance facilities. This industrial clustering can create a self-sustaining ecosystem, attracting more investment and generating employment opportunities in the long run.
In addition to capital and technology, FDI can also facilitate access to global markets for host countries. MNCs often leverage their global networks to export goods and services produced in the host country to other markets around the world. This export-oriented approach can boost a country's international trade, increase export revenues, and improve the balance of payments. Host countries can also benefit from the marketing and distribution channels of MNCs, which enable their products to reach a broader consumer base. This exposure to global markets can enhance the competitiveness and productivity of local industries.
Despite the numerous advantages, FDI can also have some negative impacts on host countries. One of the major concerns is the potential for exploitation and the asymmetrical power dynamic between multinational corporations and host governments. MNCs may prioritize their own interests over those of the host country, leading to issues such as transfer pricing, where profits are shifted to low-tax jurisdictions, and the repatriation of profits, which can result in a drain on the host country's resources. Moreover, there is a risk that the host country becomes overly dependent on foreign investors, which can leave the local economy vulnerable to external shocks.
Another potential drawback is the potential for a "brain drain" in host countries. When MNCs establish operations in a host country, they often seek skilled labor from both local and international markets. This can result in a shortage of skilled workers in the host country, as they are attracted to higher-paying jobs in foreign-owned firms. The loss of skilled labor can hinder the host country's capacity to develop its own industries and technological capabilities, creating a long-term dependency on foreign expertise.
Furthermore, FDI can have environmental implications for host countries. While MNCs may introduce advanced technologies and best practices, they can also contribute to environmental degradation if not regulated effectively. Some MNCs may take advantage of lax environmental regulations in host countries, leading to pollution, resource depletion, and unsustainable practices. Therefore, it is crucial for host governments to establish and enforce stringent environmental standards to ensure that FDI contributes to sustainable development.
The impact of FDI on a host country is largely determined by several factors. Firstly, the type of industry in which FDI is concentrated plays a significant role. Industries that are technology-intensive, such as manufacturing, information technology, and research and development, are more likely to bring in advanced technologies and contribute to skill development in the host country. On the other hand, FDI in industries such as natural resource extraction or low-skilled manufacturing may have limited positive spillover effects.
The size and scale of FDI also influence its impact on host countries. Larger investments often have a greater potential for generating positive effects. They can create more jobs, attract more suppliers and service providers, and foster more significant technological spillovers. However, it is essential to note that the impact of FDI is not solely determined by the size of the investment. The quality and nature of the investment, such as its linkages with the local economy, are equally important.
The policy environment and governance of the host country also play a crucial role in determining the impact of FDI. Countries that have transparent and stable regulatory frameworks, protection of property rights, and efficient legal systems tend to attract more FDI. Additionally, a favorable business climate, including ease of doing business, tax incentives, and investment promotion agencies, can encourage more significant investments and ensure that the benefits of FDI are maximized.
Furthermore, the skill level of the local workforce and the level of education and training opportunities available in the host country are important factors. A well-educated and skilled workforce can better absorb and utilize the knowledge and technology transferred through FDI. Host countries that invest in human capital development, such as education and vocational training, can enhance their ability to benefit from FDI and promote sustainable economic growth.
In conclusion, FDI has both positive and negative impacts on host countries. The inflow of capital, technology transfers, access to global markets, and industrial development are some of the significant benefits associated with FDI. However, concerns regarding potential exploitation, brain drain, and environmental implications need to be addressed to ensure that FDI contributes to sustainable development.

Student
Economics can be broken down into microeconomics, which looks at individual decisions, and macroeconomics, which is concerned with the economy as a whole. Both types of economics utilize historical trends and current conditions to inform business decision-making and make predictions about how markets might behave in the future. Students who choose to study economics not only gain the skills needed to understand complex markets but come away with strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Join Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive emails about new views posts, releases and updates.
Copyright 2010 - 2026 MindStick Software Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Cookie Policy