16-Dec-2022
An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies
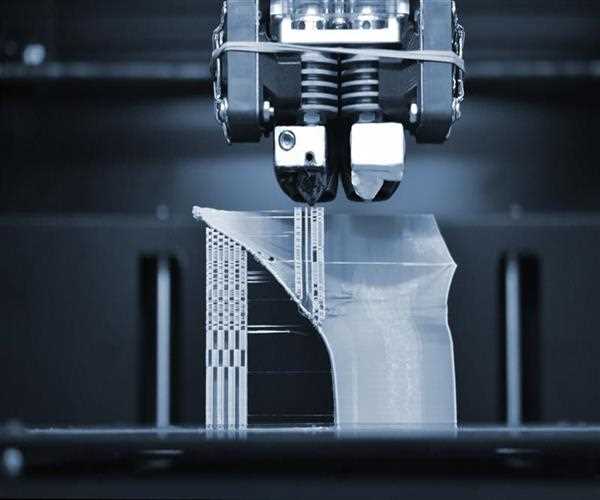
3D printing is a rapidly evolving technology that is changing the way we think about manufacturing and design. With the ability to create 3D objects from digital models, 3D printing offers a versatile and powerful tool for businesses and individuals alike. There are a variety of 3D printing technologies available on the market, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this blog post, we will give an overview of three of the most popular 3D printing technologies: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
What is 3D printing
- In 3D printing, an object is created by successively adding material in layers until the entire object is complete. This process is also known as additive manufacturing.
- 3D printing technology has been around for decades, but it has only recently become widely available and affordable for consumers. 3D printers are now capable of creating a wide variety of objects, from simple plastic toys to complex metal parts.
- There are several different technologies used in 3D printing, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common 3D printing technology is called fused filament fabrication (FFF), which uses a filament of plastic or other material that is melted and extruded layer by layer to create an object.
- Other 3D printing technologies include stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Each of these technologies has its own unique capabilities and limitations.
- 3D printing is an exciting and rapidly evolving technology with endless potential applications. It has already transformed many industries, and it will continue to do so in the years to come.
History of 3D printing
- Three-dimensional printing is a process of making a three-dimensional object from a digital file. The history of 3D printing technology can be traced back to the early 1980s, when Chuck Hull invented stereolithography (SLA).
- Since then, 3D printing technology has evolved rapidly, with new technologies and materials being developed all the time. Today, there are many different types of 3D printers available on the market, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- The most common type of 3D printer is the fused deposition modeling (FDM) printer. FDM printers work by extruding melted plastic filament through a nozzle to build up an object layer by layer. FDM printers are relatively low cost and are easy to use, making them a popular choice for home users and small businesses.
- Another type of 3D printer is the stereolithography (SLA) printer. SLA printers use lasers to cure layers of photopolymer resin, creating extremely detailed objects. SLA printers are generally more expensive than FDM printers, but they are capable of creating much higher quality prints.
- 3D printing technology is constantly evolving, and new technologies and materials are being developed all the time. This means that the possibilities for what can be created with a 3D printer are practically endless!
How does 3D printing work?
- 3D printing technology has come a long way in recent years, and there are now a variety of different ways to create three-dimensional objects. The most common type of 3D printing is known as fused deposition modeling (FDM), which uses a filament of melted plastic that is extruded through a nozzle to build up an object layer by layer.
- Another popular 3D printing technique is stereolithography (SLA), which uses a laser to cure layers of photosensitive resin into solid shapes. SLA printers are typically more expensive than FDM printers, but they can produce much finer details and smoother finishes.
- Selective laser sintering (SLS) is another type of 3D printing that uses lasers to fuse together small particles of metal, plastic, or ceramic powder into a solid object. SLS printers are often used for creating prototypes or low-volume production runs, as they can be quite expensive.
What are the different types of 3D printing technology?
- In terms of 3D printing technology, there are really only two main types: fused deposition modeling (FDM) and stereolithography (SLA). FDM is the most common type of 3D printer, and it works by extruding a plastic filament through a nozzle to build up an object layer by layer. SLA, on the other hand, works by curing a photopolymer resin with a laser to create each layer. There are also some newer technologies that are starting to become more popular, such as multi-jet printing (MJP) and selective laser sintering (SLS).
- MJP is similar to FDM in that it also extrudes multiple materials through nozzles, but it does so in a much more precise manner. This makes it ideal for creating objects with complex geometries or for printing multiple colors at once. SLS is another newer technology that uses lasers to sinter powder particles together to create an object. This Powderbed method is usually used for industrial applications due to its speed and accuracy.
Benefits of 3D printing technology
3D printing technology has revolutionized manufacturing and product development. It offers a versatile, efficient and cost-effective way to produce objects of any shape or size.
There are many benefits of 3D printing technology, including:
1. Increased Design Freedom – With 3D printing technology, there are no design limitations. You can create complex shapes and structures that would be impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
2. Faster prototyping – 3D printing allows you to quickly prototype designs and test them before moving onto production. This can save time and money in the long run.
3. Reduced Production Costs – 3D printing can save you money on production costs as it eliminates the need for costly tooling and molds.
Challenges of 3D printing technology
- 3D printing technology is still in its early developmental stages and there are a number of challenges that need to be addressed before it can be widely adopted. One of the major challenges is the high cost of 3D printers and materials. Another challenge is the lack of standardization among different 3D printing technologies, which makes it difficult to compare and choose the best option.
- Another challenge with 3D printing technology is the limited range of materials that can be used. This limits the potential applications of 3D printing and makes it less viable for mass production. Additionally, 3D printed parts often have poorer mechanical properties than conventionally manufactured parts. This is due to the fact that 3D printers typically build parts layer by layer, which can result in porous or uneven surfaces.

SEO and Content Writer
I am Drishan vig. I used to write blogs, articles, and stories in a way that entices the audience. I assure you that consistency, style, and tone must be met while writing the content. Working with the clients like bfc, varthana, ITC hotels, indusind, mumpa, mollydolly etc. has made me realized that writing content is not enough but doing seo is the first thing for it.
Join Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive emails about new views posts, releases and updates.
Copyright 2010 - 2026 MindStick Software Pvt. Ltd. All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Cookie Policy